KEYTAKEAWAYS
- Crypto wallets are a crucial element of blockchain technology, enabling users to interact with and transact on the blockchain.
- They provide access to crypto tokens, NFTs, altcoins, dApps, and other on-chain assets.
- As Web3 evolves, the management capabilities and security of wallets have become key areas of focus.

CONTENT
Explore the world of crypto wallets, from basic concepts to advanced features. Learn about different types of wallets, key management, security considerations, and popular providers. Perfect for both newcomers and experienced users in the Web3 space.
Crypto wallets are fundamental building blocks vital for Web3 and dApps to function. They are designed to interact with different blockchains and manage various token types and standards.
Key Talking Points:
1. Introduction to Crypto Wallets – Crypto Wallet Mechanism and Architecture
2. Crypto Wallet Operation – Public and Private Keys
3. Classification of Crypto Wallets
- Cold & Hot Wallets
- Custodial & Non-custodial Wallets
- Types of Crypto Wallets
4. Crypto Wallet Service Providers – Consumer Wallets
In traditional financial and banking systems, bank accounts serve as the interface through which we access financial services, conduct transactions, and participate in the global financial ecosystem.
Similarly, crypto wallets are applications that allow users to interact with the blockchain by authorizing, validating, and managing transactions. Based on their technical capabilities, these wallets enable users to access various tokens, NFTs, meme coins, and other digital assets across multiple blockchains.
This article focuses on end-user crypto wallets, but we will also discuss Institutional Wallet Infrastructures used to manage funds at larger organizations such as crypto exchanges, OTCs, NFT marketplaces, Automated Market Makers, neo-banks, and similar entities.
CRYPTO WALLET OPERATIONS
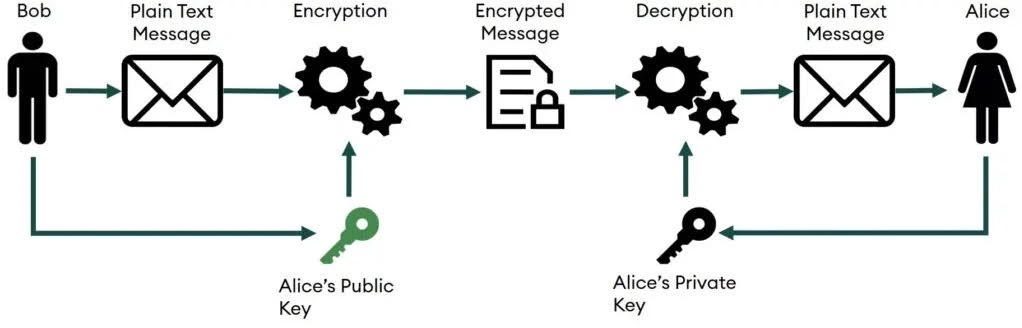
Crypto wallet applications operate on a cryptographic principle called asymmetric encryption. This involves a cryptographic key pair, consisting of:
Public Key
A public key serves as a user’s identifier and is used to create the public wallet address, effectively functioning as the wallet’s public identity on the blockchain. It acts as an address that others can reference to verify the authenticity of all transactions associated with that particular wallet.
Private Key
This is essentially your signature of authenticity. It enables you to receive tokens and authenticate your crypto transactions. This key is crucial for accessing your assets, so it must be backed up securely to prevent being locked out of your wallet.
Source: AMINIA
Crypto wallet service providers typically recommend that users set and remember a seed phrase, which can be used to recover their wallet keys if needed. The combination of the public and private keys constitutes a crypto wallet. Asymmetric encryption is the fundamental concept driving blockchain technology. Please follow this link to learn more about asymmetric encryption.
CLASSIFICATION OF CRYPTO WALLETS
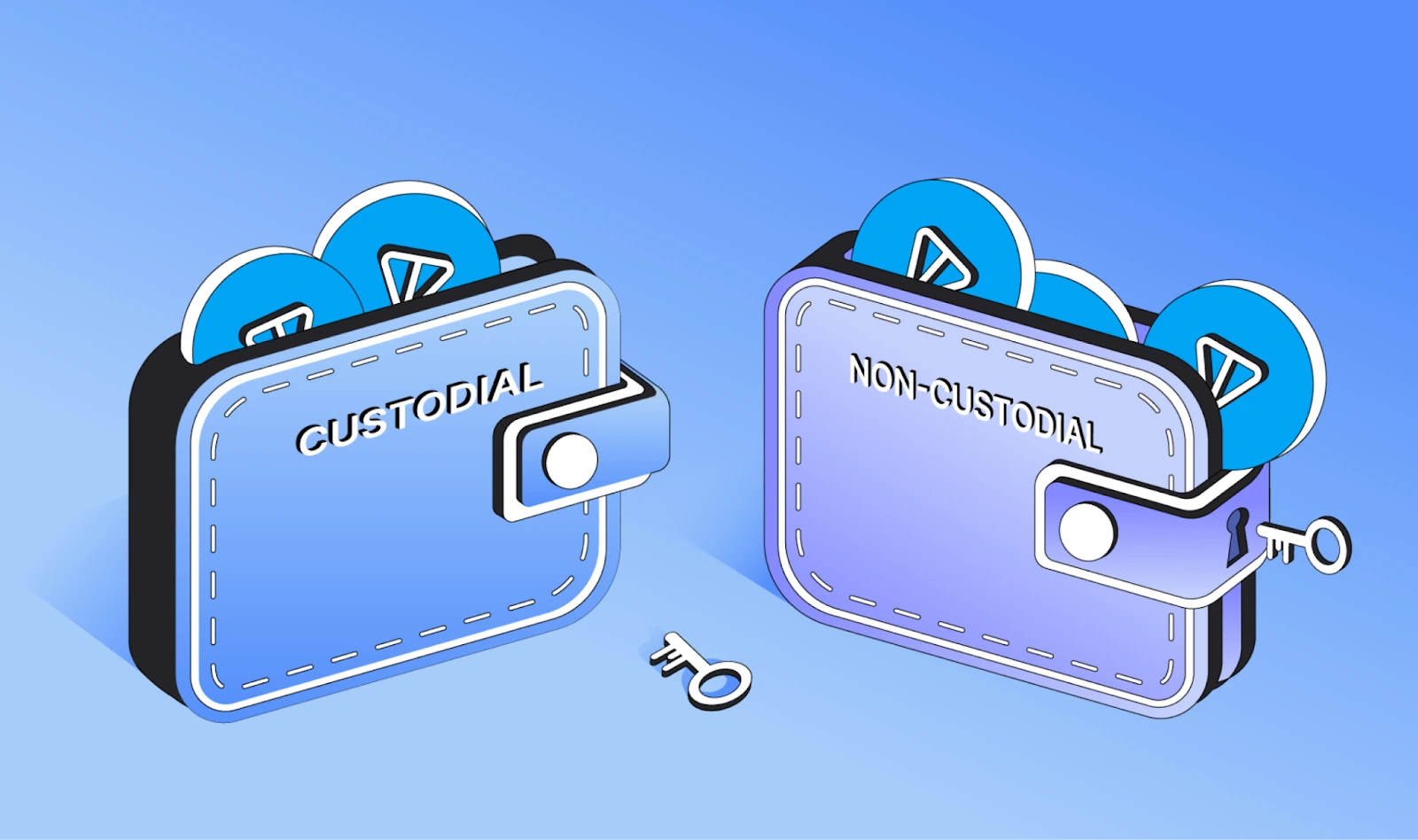
i. Based on private key management, wallets are divided into two types
- Custodial Wallets
- Non-Custodial Wallets
Source: TON Blog
Custodial Wallets
These are systems where a third-party service provider generates and manages private keys on behalf of users. These wallets are typically easier to set up and use, often relying on standard authentication methods like passwords and OTPs for transactions. They also offer recovery options for passwords and keys, similar to how online services like email handle account recovery.
However, while custodial wallets alleviate the burden of managing private keys, they have certain drawbacks. Since the private keys are controlled by the third-party provider, the wallet’s security depends entirely on the provider’s security practices. Additionally, custodial wallets offer less privacy, as funds are stored on infrastructure controlled by a third party.
Non-Custodial Wallets
These crypto wallets allow users to retain full ownership and control of their private keys. In other words, the wallet is entirely under the user’s control, providing complete access to stored tokens. Non-custodial wallets are generally considered more secure and less vulnerable to hacks, as there is no third-party custodian involved.
These crypto wallets are ideal for users who are technically proficient in cryptocurrency, value privacy, and understand the security risks involved in managing private keys. Many wallet providers offer key recovery options, typically requiring a passphrase that users must either remember or securely store to regain wallet access if necessary.
ii. Based on use cases, wallets can also be divided into two categories:
Cold Wallets
These are typically physical devices resembling flash drives. They are called “cold” because they are not constantly connected to the internet and are used infrequently for transactions. Cold wallets are primarily designed for individuals and businesses to securely store private keys for wallets holding significant amounts of digital assets. Due to their offline nature, cold wallets are less vulnerable to hacking, making them a highly secure option for protecting large reserves of cryptocurrency or other digital assets.
Hot Wallets
These are software applications that maintain constant internet connectivity, making them convenient for individuals and businesses with frequent transactions and lower transaction volumes. Due to their online nature, hot wallets are more vulnerable to cyberattacks and social engineering tactics, making them less secure than cold wallets. However, their ease of use and accessibility make them a popular choice for day-to-day transactions.
TYPES OF CRYPTO WALLETS
Wallet applications are implemented in various ways:
Browser-Based Crypto Wallets
These wallets are accessed via web browsers or browser extensions, such as MetaMask, Brave Wallet, and Trust Wallet.
Mobile Crypto Wallet Apps
Standalone apps downloadable on smartphones, tablets, and other devices, storing private keys directly on the device.
Miniapps
Wallets available as miniapps within platforms like Telegram, powered by the TON blockchain.
Embedded Wallets
Provided by service providers like crypto exchanges, online gaming platforms, NFT marketplaces, and OTC platforms as part of their user accounts.
Hardware Wallets
Physical devices, similar to flash drives, that store private keys offline, offering the highest level of security.
CRYPTO WALLET SERVICE PROVIDERS
Let’s examine some popular wallet service providers:
MetaMask Wallet
MetaMask is one of the market’s most popular wallets. It is a non-custodial, hot wallet available as both a browser extension and a mobile app.
Source: MetaMask
MetaMask offers various features, including buying, selling, swapping, transferring, staking, and receiving tokens. It also supports cross-chain bridges, enabling seamless token transfers between different blockchains. Additionally, MetaMask integrates with NFT marketplaces like OpenSea, allowing users to easily buy and sell NFTs. With robust support for DeFi and a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps), MetaMask is a versatile and widely-used wallet for everyday users. One potential drawback is its varying gas fees for different digital assets.
To see a complete list of features, please visit the MetaMask site.
Trust Wallet
Trust Wallet is another prominent Web3 wallet available as a standalone mobile app and browser extension. It is a hot wallet with approximately 140 million users globally. This simple, seamless, and user-friendly wallet supports 10M+ assets, 600M+ NFTs, DeFi, and 100+ blockchains.
With strong security practices in place, Trust Wallet offers:
- An independently audited wallet (by industry leaders) that is ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 certified
- Strong encryption using the latest AES encryption standards
- Security monitoring to protect users from risky transactions and ensure a safe Web3 experience
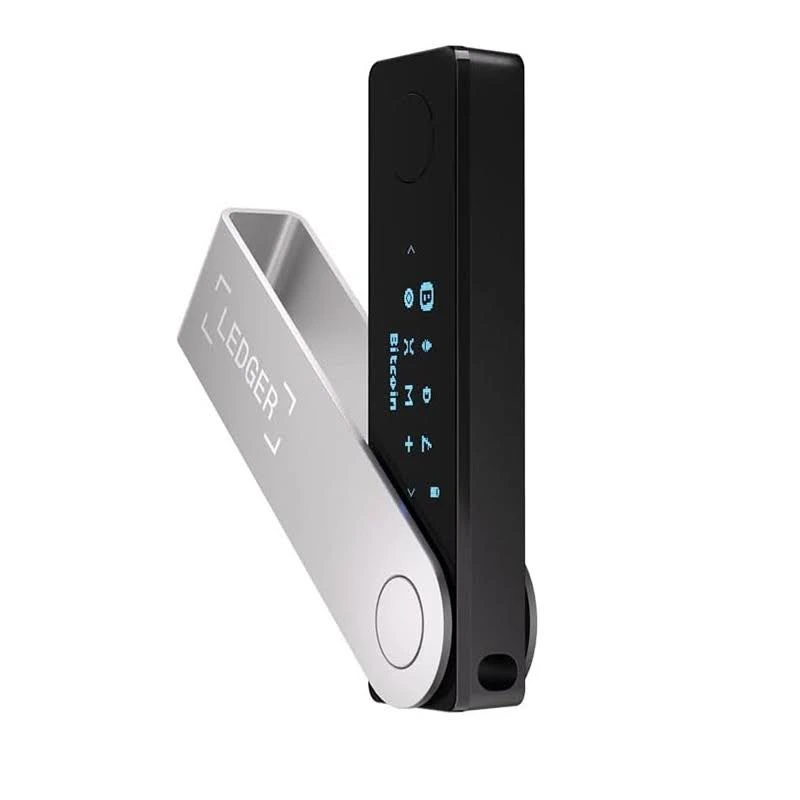
Ledger Wallet
Ledger is a cold wallet that securely stores private keys on a hardware device, providing enhanced protection. It integrates with existing software hot wallets to enable access to these private keys. Users can now conduct transactions via their software hot wallets with a minimized risk of private key compromise.
Compatible with various hot wallet services, Ledger supports a wide range of digital assets, including NFTs and ERC-20 tokens. Ledger has made significant progress in expanding its product offerings. Initially a simple USB device resembling a flash drive designed to integrate with software wallets on computers and mobile devices, Ledger now offers touchscreen devices with NFC capabilities, allowing seamless integration with mobile wallets for greater convenience and security.
- Have a look at their impressive range of products here.
- List of tokens support by Ledger can be found on this link.
- A list of wallet services provided by Ledger can be found here.
Coinbase Wallet
Coinbase is a leading cryptocurrency exchange for buying, selling, storing, and managing digital assets, ranking third in trading volume. Coinbase Wallet expands its services by enabling users to manage tokens, NFTs, and multiple wallets across various blockchain networks like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, and DeFi protocols.
The platform prioritizes security with features like biometrics, passwords, and security locks, and its browser extension supports Ledger hardware wallets for added protection.
Learn more about Coinbase Wallet on their site.
THE ROAD AHEAD: CRYPTO WALLET ADOPTION AND GROWTH
In 2022, global crypto wallets exceeded 80 million, up from 5.78 million in 2016. Bitcoin wallet users are projected to grow from 32 million in 2021 to 200 million by 2024. The global crypto wallet market, valued at $8.42 billion in 2022, is expected to grow at a 24.8% CAGR through 2030. These trends signal significant opportunities for crypto wallet providers, with future wallets set to be more secure, user-friendly, and integrated with Web3.
▶ Buy Crypto at Bitget
CoinRank x Bitget – Sign up & Trade to get $20!