KEYTAKEAWAYS
- Bybit Loses $1.5 Billion in Crypto Assets in Theft, Setting Record for Largest in Crypto History
- Bybit Theft Triggers Market Panic, Crypto Market Cap Plummets 19.27% in One Week
- Review of 15 Major Security Incidents in Crypto History

CONTENT
On February 21, 2025, the cryptocurrency industry was once again shaken by a major security incident—leading exchange Bybit lost $1.5 billion in assets due to a social engineering attack. This incident not only became one of the largest single thefts in cryptocurrency history but also exposed the vulnerability of exchange security management.
This research report will analyze in detail the background, timeline, and response measures of the Bybit theft incident, as well as review the top ten exchange security incidents in crypto history, exploring common attack methods and industry response strategies.
BYBIT LOSES $1.5 BILLION IN CRYPTO ASSETS IN THEFT, SETTING RECORD FOR LARGEST IN CRYPTO HISTORY
On February 21, on-chain detective Zachxbt monitored suspicious fund outflows from Bybit. On-chain records showed a multi-signature address transferred approximately $1.5 billion worth of ETH and converted LSD assets to native ETH through DEXs. Shortly after, Bybit’s CEO released a statement confirming that hackers had taken control of a specific ETH cold wallet involving over 500,000 ETH.

Bybit Theft Incident Review
February 21
- 23:27: On-chain detective Zachxbt monitored suspicious fund outflows from Bybit, exceeding $1.46 billion in total.
- 23:44: Bybit CEO Ben Zhou confirmed an ETH cold wallet was controlled by hackers, with funds transferred to unconfirmed addresses.
- 23:53: Bybit officially announced that hackers transferred funds by exploiting Safe multi-signature system vulnerabilities through a fake transaction interface.
February 22
- 0:20: Bybit CEO announced a livestream to address the incident.
- 9:08: Safe officially responded that no code repository breach was found, but some functions were suspended.
- 15:21: Bybit detected hackers attempting to transfer assets via Chainflip and called on cross-chain bridge projects to assist in blocking.
February 23
- 14:55: Bybit stated deposits and withdrawals had fully returned to normal levels
- 23:41: Bybit announced successful freezing of $42.89 million in stolen funds, thanking multiple parties for assistance.
February 24
- 15:39: Bybit claimed ETH reserves were close to 100% with deposits and withdrawals restored to normal
- 18:12: According to lmk.fun monitoring, Bybit hackers were using multiple DEXs to convert ETH to DAI
February 25
- 19:09: According to Ember monitoring, Bybit hackers had laundered 89,500 ETH (approximately $224 million), representing 18% of the total stolen ETH (499,000).
- 22:40: Bybit launched a Lazarus hacker group bounty website, offering 5% rewards to contributors helping track funds
February 26
- 9:35: Bybit hackers had cumulatively laundered 135,000 ETH
- 23:16: Safe released an interim report confirming the attack was achieved through compromising developer devices, with no vulnerabilities in contract or frontend code.
February 27
- 9:25: On-chain data showed hackers had laundered 206,000 ETH, with 292,000 remaining.
- 18:12: FBI confirmed the $1.5 billion Bybit theft was carried out by North Korean hacker group Lazarus Group.
February 28
- 9:25: Bybit hackers had cumulatively laundered 270,000 ETH
Bybit Appears to Have Successfully Weathered Its Trust Crisis
After suffering a $1.5 billion hack, Bybit exchange faced an unprecedented trust crisis. However, through swift and effective response measures, Bybit not only successfully stabilized the situation but also won widespread recognition from users and the industry.
Following the incident, Bybit quickly experienced a massive wave of withdrawal requests. Facing user panic, Bybit efficiently processed over 350,000 withdrawal requests within 72 hours, demonstrating its strong technical capabilities and liquidity. Bybit CEO Ben Zhou shared the entire crisis response process in detail during an AMA, emphasizing that the exchange always prioritizes user asset security.
To compensate for the stolen funds, Bybit rapidly raised capital through various means, including loans, large user deposits, and market purchases. According to the latest data, Bybit has obtained approximately 446,870 ETH, almost completely covering the lost amount. This measure not only ensured the platform’s normal operations but also conveyed to users that Bybit possesses strong solvency.
During the crisis, Bybit received strong support from multiple industry institutions. Exchanges such as Bitget, MEXC, and Binance provided liquidity assistance, helping Bybit through difficult times. Additionally, Bybit launched a bounty website targeting the Lazarus hacker group, promising 10% of recovered funds as rewards to incentivize global security experts to assist in tracking and freezing stolen assets.
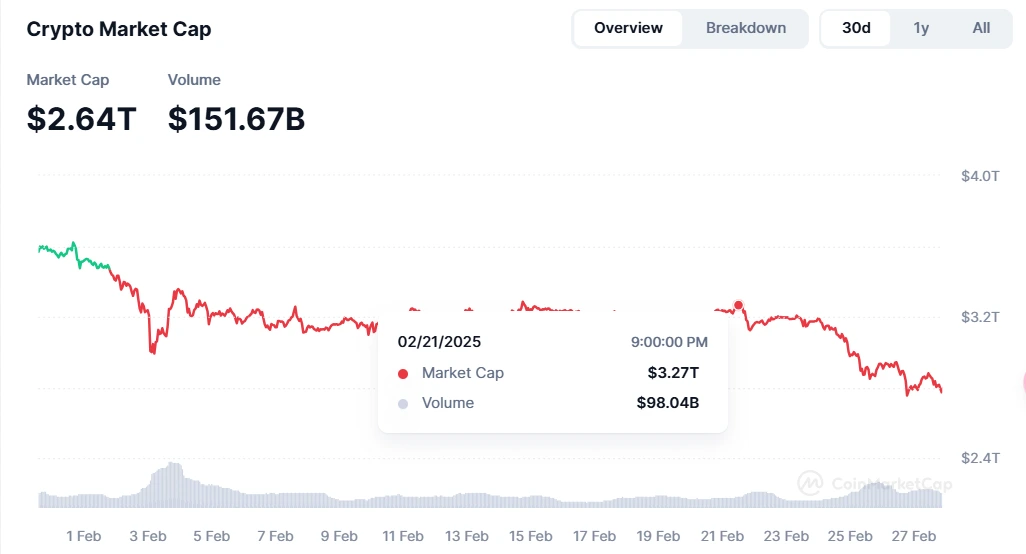
Bybit Theft Triggers Market Panic, Crypto Market Cap Plummets 19.27% in One Week
The $1.5 billion hack of Bybit exchange triggered extreme panic in the cryptocurrency market, leading to widespread sharp declines in cryptocurrency prices throughout the week. According to CoinMarketCap data, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization plunged from $3.27 trillion on February 21 to $2.64 trillion on February 28, a drop of 19.27% in just 7 days.
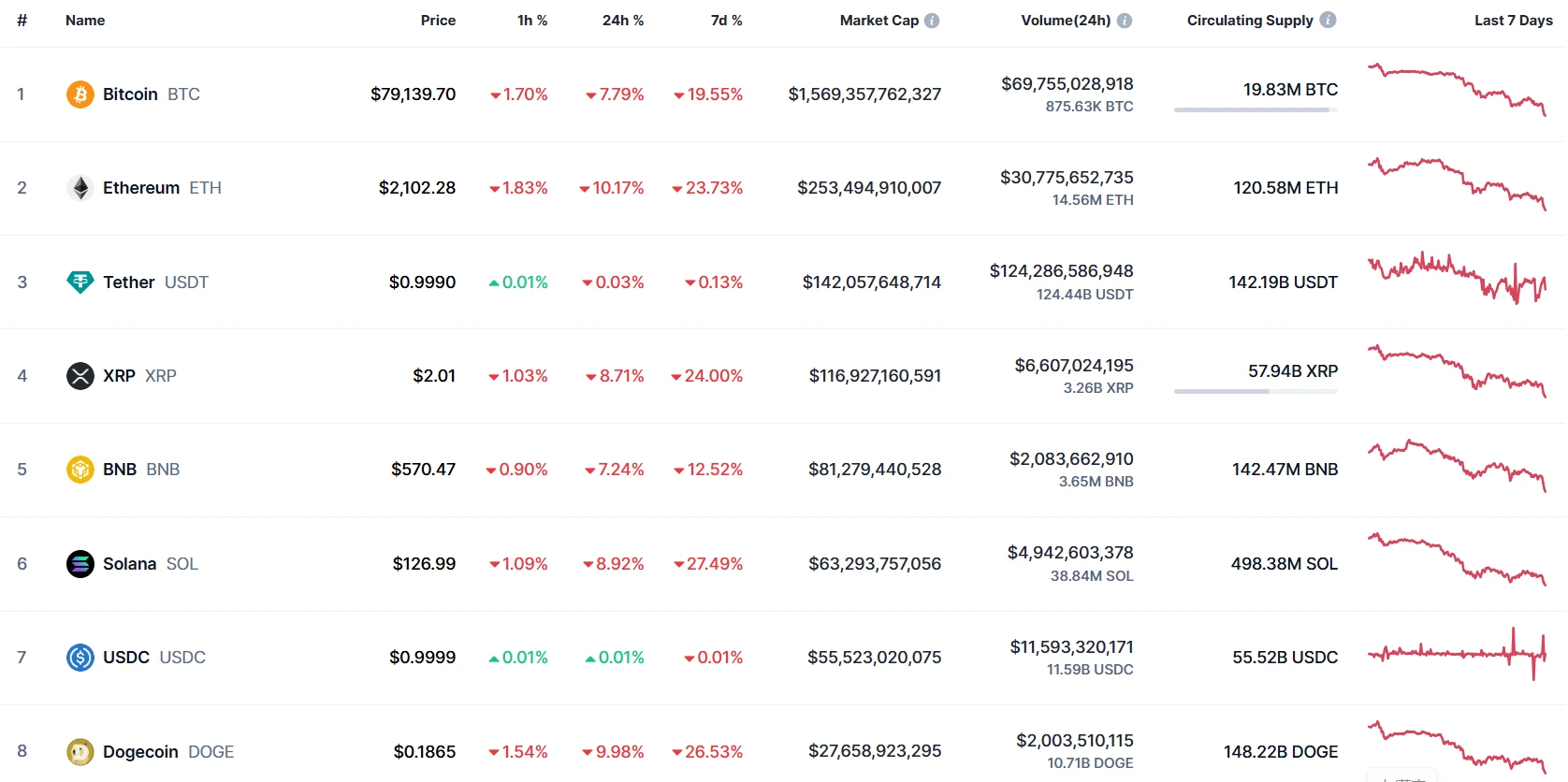
Leading Cryptocurrency Prices Broadly Hit:
- Bitcoin (BTC): Priced at $79,139, down 19.55% in one week, marking the largest weekly drop in nearly six months.
- Ethereum (ETH): Price significantly retreated to $2,102, falling by 23.73%, making it one of the worst-performing mainstream assets this week.
- XRP: Price slid to $2.01, dropping 24%, with extremely low market sentiment.
- BNB: Priced at $570, down 12.52%, showing a relatively smaller decline but reflecting market caution toward centralized exchange assets.
- Solana (SOL): Crashed to $126.99, down 27.49%, becoming one of the worst-performing major cryptocurrencies this week.
REVIEW OF 15 MAJOR SECURITY INCIDENTS IN CRYPTO HISTORY
This section examines the most influential security incidents in cryptocurrency history, from exchange hacks that shocked the industry to exposures of systemic vulnerabilities. The cryptocurrency world has experienced unprecedented turbulence and challenges. Through reviewing 15 major security incidents, we see not only losses totaling tens of billions of dollars but also reveal the vulnerabilities in cryptocurrency ecosystem security.
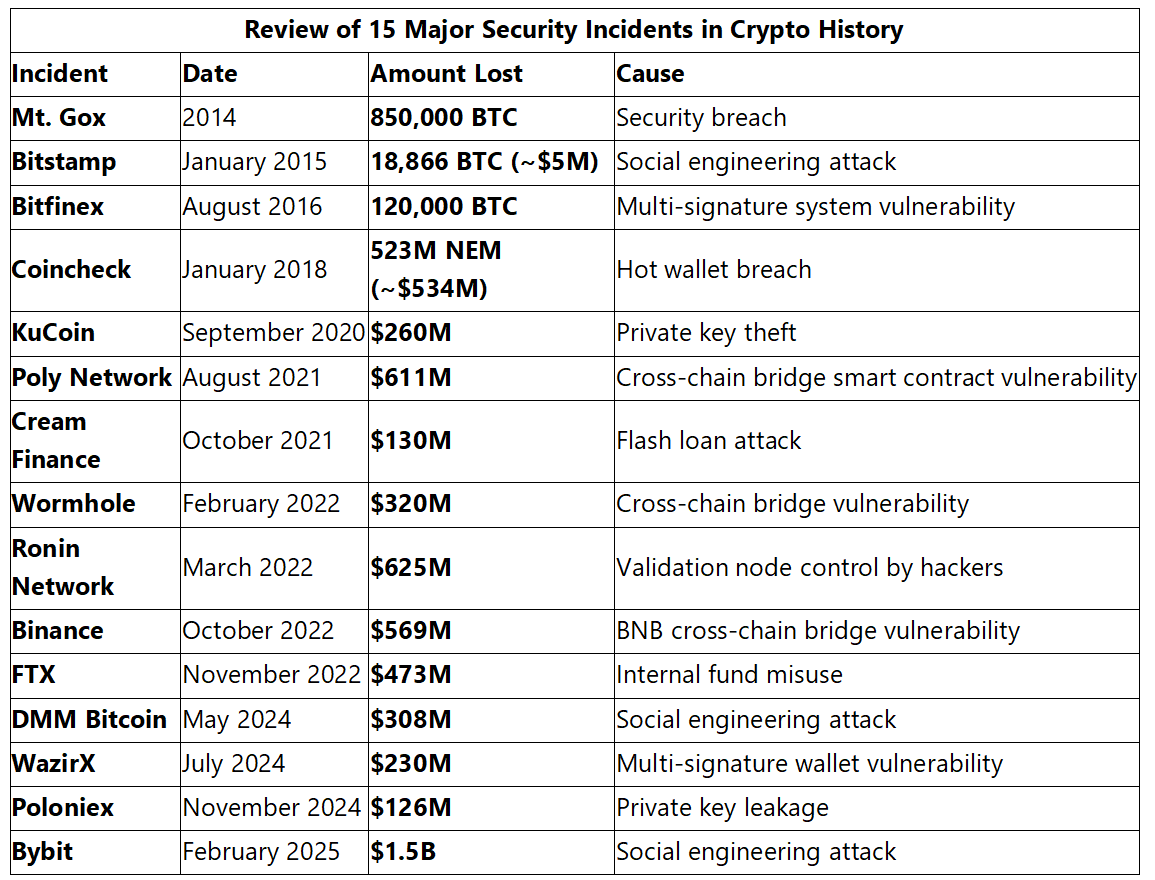
1. Bybit (February 21, 2025)
On February 21, 2025, Bybit lost $1.5 billion in a social engineering attack, becoming the largest single theft in cryptocurrency history. The incident exposed vulnerabilities in cold wallet management and multi-signature systems, driving industry demand for advanced security protection technology.
2. Poloniex (November 2024)
In November 2024, Poloniex exchange suffered a hacker attack due to internal management vulnerabilities leading to private key leakage, with approximately $126 million in crypto assets stolen. Hackers used obtained private keys to access funds stored in cold wallets, stealing large amounts of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies.
3. WazirX (July 2024)
Indian CEX WazirX suffered a major wallet vulnerability attack on July 18, 2024, resulting in unauthorized transfers of over $230 million in crypto assets. The attack targeted WazirX’s multi-signature wallet on Ethereum. Over $100 million in Shiba Inu (SHIB), 20 million MATIC tokens ($11 million), 640 billion PEPE tokens ($7.5 million), 5.7 million USDT, and 135 million GALA tokens ($3.5 million) were stolen.
4. DMM Bitcoin (May 2024)
In May 2024, DMM Bitcoin exchange suffered a social engineering attack, resulting in theft of approximately $308 million in crypto assets. Hackers successfully obtained internal employee credentials and access rights through carefully planned social engineering methods, accessing both cold and hot wallets.
5. FTX (November 2022)
In November 2022, FTX lost $473 million due to internal fund misuse, ultimately leading to exchange bankruptcy. The incident exposed transparency issues with centralized exchanges, triggering profound industry reflection on regulation and internal management.
6. Binance (October 2022)
In October 2022, Binance lost $569 million due to BNB cross-chain bridge vulnerabilities. Binance quickly suspended bridge services and froze some funds. The incident prompted increased industry focus on cross-chain bridge security.
7. Ronin Network (March 2022)
In March 2022, Ronin Network lost $625 million when hackers controlled validation nodes. The incident severely impacted the Axie Infinity ecosystem. North Korean hacker group Lazarus Group was accused, driving upgrades to node security mechanisms.
8. Wormhole (February 2022)
Wormhole is a cross-chain bridge protocol designed to connect multiple blockchains, allowing assets to flow between different chains. In February 2022, Wormhole lost $320 million in wETH tokens due to cross-chain bridge vulnerabilities. Although all funds were recovered, the incident highlighted cross-chain bridges’ security risks, prompting the industry to strengthen cross-chain technology auditing and monitoring.
9. Cream Finance (October 2021)
In October 2021, decentralized finance platform Cream Finance suffered a flash loan attack, with hackers exploiting platform vulnerabilities to launch a complex attack resulting in losses of approximately $130 million. Through flash loan operations, attackers manipulated market prices, triggering system vulnerabilities. The incident exposed DeFi protocols’ vulnerabilities in complex financial operations.
10. Poly Network (August 2021)
In August 2021, Poly Network lost $611 million due to cross-chain bridge smart contract vulnerabilities. Surprisingly, the hacker eventually returned most funds, but the incident exposed security risks in cross-chain technology, driving improvements in cross-chain bridge security standards.
11. KuCoin (September 2020)
In September 2020, KuCoin suffered a hack resulting in losses of approximately $260 million in digital assets. Hackers accessed hot wallets and withdrew funds by stealing private keys. KuCoin quickly initiated asset recovery and preventive measures, resuming platform operations shortly after the incident.
12. Coincheck (January 2018)
In late January 2018, prominent Japanese cryptocurrency exchange Coincheck suffered one of the most severe centralized exchange hacks in history. Hackers infiltrated the exchange’s hot wallet, stealing 523 million NEM tokens worth approximately $534 million at the time. The incident prompted Japan’s Financial Services Agency to strengthen regulations, led to Coincheck’s acquisition by Monex Group, and drove improvements in hot wallet management technology.
13. Bitfinex (August 2016)
In August 2016, Bitfinex was attacked due to vulnerabilities in its multi-signature security system. Hackers exploited flaws in BitGo-supported security protocols to illegally withdraw 120,000 bitcoins from hot wallets. The exchange compensated users for losses by issuing tokens (BFX) and strengthened multi-signature system security.
14. Bitstamp (January 2015)
In early 2015, Bitstamp suffered a targeted social engineering attack. Hackers accessed a system administrator account through malicious files, successfully obtaining critical wallet.dat files and passwords. Despite the exchange’s rapid response, 18,866 bitcoins (approximately $5 million) were lost. This incident highlighted the importance of employee security awareness training.
15. Mt. Gox (2014)
As the once-largest Bitcoin exchange globally, Mt. Gox experienced the most destructive security incident in cryptocurrency history in 2014. The theft of approximately 850,000 bitcoins not only caused Bitcoin prices to plummet but also triggered profound reflection on the security of centralized exchanges. This landmark event ultimately led to Mt. Gox’s bankruptcy, with impacts continuing to this day.
HOW CRYPTO SECURITY INCIDENTS HAPPEN
Security incidents in the cryptocurrency field occur frequently, with complex and diverse underlying causes. Through in-depth analysis of major security incidents, we find these events primarily stem from technical vulnerabilities, human factors, management issues, and constantly evolving hacking techniques. As the Web3 industry rapidly develops, the forms and scale of security threats continue to evolve.
Technical vulnerabilities are among the most common security threats in the cryptocurrency field, typically manifesting as code defects, system design issues, or improper private key management.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: As the core of blockchain applications, smart contracts are easily exploited by hackers when vulnerabilities exist. For example, in the 2021 Poly Network incident, hackers exploited cross-chain bridge smart contract vulnerabilities to steal $611 million. This incident exposed cross-chain technology’s security deficiencies, driving industry emphasis on smart contract auditing.
- System Design Flaws: System design flaws may provide opportunities for hackers. In the 2016 Bitfinex incident, hackers exploited vulnerabilities in its multi-signature system to steal 120,000 bitcoins. This incident prompted exchanges to reassess multi-signature system security and drove stricter security standards.
- Improper Private Key Management: Private keys are core to cryptocurrency assets; poor management can lead to catastrophic consequences. The 2020 KuCoin incident and 2024 Poloniex incident both resulted from private key leaks, with losses of $260 million and $126 million respectively. These incidents highlight the importance of private key storage and access control.

Social engineering attacks gain sensitive information by manipulating human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities, representing an increasingly serious threat in the cryptocurrency field.
- Phishing Attacks: Hackers impersonate trusted entities to trick victims into providing sensitive information. In the 2015 Bitstamp incident, hackers successfully obtained system administrator credentials through malicious file implantation, resulting in 18,866 bitcoins being stolen.
- Credential Theft: Employee credential leaks may provide hackers with direct access. In the 2024 DMM Bitcoin incident, hackers obtained internal employee credentials through carefully planned social engineering methods, stealing $308 million.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APT): APT attacks typically target specific targets with long-term, covert penetration. In the 2025 Bybit incident, hackers stole $1.5 billion through an APT attack, becoming the largest single theft in cryptocurrency history.
Of course, poor internal management is the root of many security incidents, including insufficient access control, fund management vulnerabilities, and lack of security audits.
- Insufficient Access Control: Improper permission allocation may lead to critical system abuse. In the 2022 Ronin Network incident, hackers stole $625 million by controlling validation nodes, exposing weaknesses in node permission management.
- Poor Fund Management: Internal fund management vulnerabilities may lead to asset loss. In the 2022 FTX incident, internal fund misuse resulted in $473 million in losses, ultimately bankrupting the exchange and raising widespread questions about centralized exchange transparency.
- Lack of Security Audits: Many security incidents expose pre-incident audit deficiencies. For example, both Cream Finance and Wormhole incidents resulted from failures to detect vulnerabilities in time, with losses of $130 million and $320 million respectively.
Hacker attack methods continuously evolve. As cryptocurrency technology develops and crypto financial economic models evolve, hackers also research and develop many new attack methods.
- Flash Loan Attacks: Flash loans allow attackers to borrow large amounts without collateral to manipulate market prices or trigger system vulnerabilities. In the 2021 Cream Finance incident, hackers stole $130 million through flash loan attacks exploiting price manipulation vulnerabilities.
- Cross-Chain Bridge Attacks: Cross-chain bridges connecting different blockchains have become key hacker targets. In the 2022 Wormhole and Binance incidents, hackers exploited cross-chain bridge vulnerabilities to steal $320 million and $569 million respectively.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Attacks targeting third-party service providers are increasing. For example, some exchanges have been compromised due to reliance on insecure third-party services.
From the attacker perspective, cryptocurrency’s high value attracts professional criminal organizations and even state-level hacker teams.
- State-Level Hacker Groups: In the 2022 Ronin Network incident, North Korean hacker group Lazarus Group was accused of stealing $625 million. This incident indicates state-level hacker groups have become significant threats in the cryptocurrency field.
- Professional Criminal Gangs: In many security incidents, hackers demonstrate high professionalism and organization. For example, in the Bybit incident, hackers successfully stole $1.5 billion through carefully planned social engineering attacks.
- Darknet Fund Transfers: Stolen funds are typically laundered and transferred through the darknet. For example, in the Mt. Gox incident, 850,000 stolen bitcoins were transferred and laundered through complex darknet channels.
Frequent security incidents in the cryptocurrency industry not only expose technical and management weaknesses but also reveal challenges faced during rapid industry development. From technical vulnerabilities to social engineering attacks, from internal management issues to new attack methods, security threats continue to evolve in form and scale.
Through the Bybit incident, we see industry unity and resilience. Whether through liquidity support between exchanges or coordinated defense by security institutions, the crypto industry demonstrates strong cohesion in facing crises. In the future, only through technological innovation and industry collaboration can user losses be minimized when security incidents occur.
▶ Buy Crypto at Bitget
CoinRank x Bitget – Sign up & Trade to get $20!


















