KEYTAKEAWAYS
-
Nvidia’s Q2FY24 report revealed impressive results, surpassing market expectations with a gross profit margin exceeding 70%, driven by robust demand for data center AI chips.
-
Despite a current stock price of $454.61 per share, the evaluation using PE and PEG ratios suggests potential overvaluation. However, analysts remain optimistic about Nvidia’s future growth and performance in the AI industry.
-
Nvidia’s focus on GPU-based accelerated computing and the introduction of products like L40S reflect its strategic response to evolving market demands, aiming to make AI services accessible to a wider range of businesses.

CONTENT
Do you remember the highly anticipated Nvidia earnings report on August 23rd? It was a standout performance, with a gross profit margin exceeding 70%. Nvidia’s CEO, Jensen Huang, explicitly stated, ‘A new era of computing has begun, with companies worldwide transitioning from general-purpose computers to high-speed and generative AI.’
Furthermore, the company’s forecast for the third quarter suggests further growth, reaching $16 billion in revenue, with an even higher gross profit margin. With the upcoming release of the third-quarter earnings report, is it safe to say that Nvidia is having its ‘iPhone moment’ in the AI industry? Can Nvidia’s extraordinary financial projections provide a boost to the global AI industry once again?
Before venturing into the AI industry, investors may want to know, ‘What is Nvidia?’ and ‘Is the stock price affordable?’ What are the future industry trends? Today, the article will embark on a data-driven journey and share some insights about Nvidia. Let’s get it started!
NVIDIA CORPORATION OVERVIEW
NVIDIA Q2FY24 FINANCIAL REPORT ANALYSIS
From the Q2FY24 financial report, Nvidia announced its results on August 23, 2023, covering the period from May 2023 to July 2023. The company’s revenue and EPS exceeded market expectations by a significant margin. Additionally, the Q3FY24 revenue forecast of $16 billion for August 2023 to October 2023 is 28% higher than market predictions. The primary reason behind this outstanding performance is the strong demand for data center AI chips, which has led to impressive financial results.
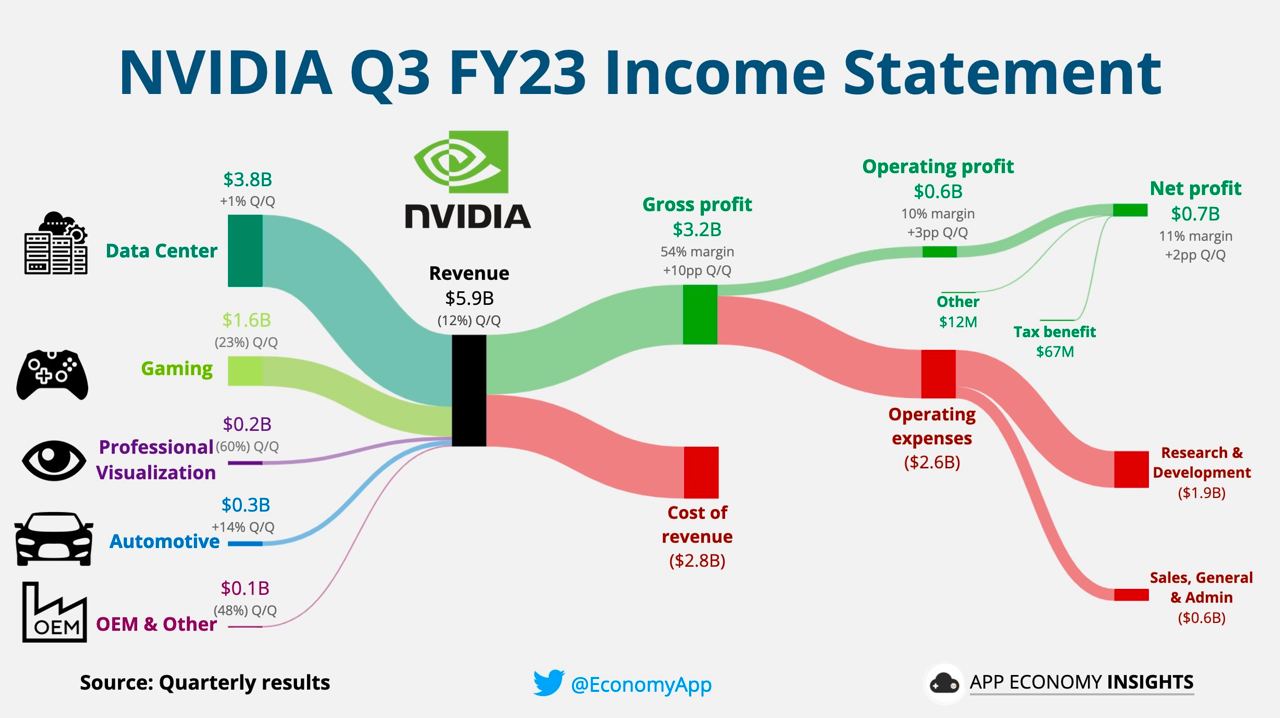
(Source: App Economy Insights)
Looking at Nvidia’s business segments, as shown in the chart, it is divided into five major sectors: data center, gaming, professional visualization, automotive, OEM & others. Currently, the primary source of revenue comes from the data center sector. This aligns with the company’s external emphasis on the fact that “demand in data centers will only continue to grow and become more complex in the future.” Cloud service providers are actively purchasing HGX100, A100, and other pre-systems, indicating strong demand and driving the growth of the data center business.
Unlike the cryptocurrency mining period, where graphics card sales led to Nvidia’s substantial increase in revenue, this robust demand is seen by the market as the emergence of a new demand that could usher in the next technological revolution.
IS NVIDIA’S STOCK PRICE CHEAP?
On January 22, 1999, Nvidia had its initial public offering (IPO) with a stock price of $12 per share. Currently, as of October 13, 2023, NVDA’s stock price is $454.61 per share. Clearly, over the long term, Nvidia’s stock price has been on an upward trend, resembling a bullish market that keeps moving upwards. Particularly, when the company reported exceptional first-quarter earnings in May, it triggered a significant rise in the stock price. However, after the initial excitement, the market has returned to a state of relative calm. So, is Nvidia’s stock price considered expensive or not? How should investors evaluate it? It’s quite simple, and you can estimate it using the PE and PEG ratios, for which the formulas are provided below:
- PE (Price-to-Earnings) = Stock Price / Earnings Per Share (EPS)
- PEG (Price/Earnings-to-Growth) = PE Ratio / Earnings Per Share Growth Rate (EPS Growth Rate)
Please note that the PEG ratio is used to assess a stock’s valuation relative to its earnings growth. It is commonly employed to determine whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued. The market often uses future growth potential as a basis for evaluating whether a company is worth investing in.
If we use the second-quarter financial report to estimate and assume that the cumulative EPS for all four quarters will be 8.26 (0.82 + 2.48 + 2.48 + 2.48), considering the current stock price of 454.61, the PE ratio is approximately around 55. This might seem relatively high when compared to the market’s average PE ratio of 30 for related industries. However, stock prices are often regression to the mean.Taking into account the earnings growth potential for Nvidia in 2024, if we approach this from a PEG perspective and gather relevant data to estimate using the formula, investors might obtain a very different answer. It’s essential to remember that investments are based on future prospects and forward-looking perspectives.
THE HOT STREAK OF NVIDIA: THE REIGN OF CHIPS
Nvidia’s high-performance chips underwent two expansion phases. One was during the Bitcoin boom in 2021 when the cryptocurrency’s price soared from $13,000 to $65,000. The second was ushered in by ChatGPT, opening a new era in AI. With various countries gearing up in the AI arms race, the market anticipates a 33% compound annual growth rate in the AI computing market from 2023 to 2027. This surge in demand has outpaced Nvidia’s chip production capacity.
Nvidia believes that the global multi-trillion-dollar data center industry is transitioning towards accelerated computing. This shift aims to meet the demands for higher efficiency, energy savings, and lower costs compared to traditional CPU-based general-purpose computing. The focus is moving towards GPU-based accelerated computing, where CPUs and GPUs are combined into superchips. The development of generative AI is driving this transition trend. If Nvidia’s perspective is accurate, this transformation is expected to yield long-term benefits, beyond the effects of generative AI alone.
NVIDIA’S STRONG PERFORMANCE
Nvidia’s impressive performance in the July quarter results and its robust guidance for the October quarter have led to positive reactions from analysts. As a result, one analyst from Morgan Stanley raised the earnings outlook for Nvidia, with an estimated 49% growth for data center GPU shipments in 2023, an 89% increase in 2024, and a 78% rise in 2025. The figure provided in Exhibit 4 reflects the analyst’s predictions for Nvidia’s HGX and DGX unit shipments.
- Use of Nvidia’s High-Performance Chips:
By examining the production estimates for the Asian semiconductor supply chain in the fourth quarter of 2023, we can see that there is a projected output of approximately 800,000 to 900,000 units of the H100 GPU module. This exceeds the market’s initial expectation of 600,000 to 700,000 units. According to Morgan Stanley analyst Joe Moore, there may be a time lag from GPU module production to AI servers and, ultimately, to Nvidia’s revenue. Considering the revenue forecast and H100 demand, the analyst still sees room for upward adjustments in Nvidia’s revenue prediction or a potential supply chain correction in the latter half of 2024. However, AI capital expenditure demand remains a critical uncertainty.
- Discussion of Nvidia’s Key Customers:
Among Nvidia’s many customers, three primary categories require the computational power of H100 or A100: cloud service providers like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft; AI software service companies like OpenAI; and companies with data integration needs such as Tesla and financial institutions. With the rapid expansion of the data and information era, the demand for computing power will only continue to grow. However, the capacity for production is currently constrained to a few key suppliers, including memory technology provider SK Hynix (for GPU memory technology HBM) and semiconductor foundry TSMC (for CoWoS packaging technology). The critical question is not about demand but rather the extent to which production capacity can meet the market’s needs.
It is worth noting that in recent years, the most significant AI demand in the market has been for large-scale language models, ultimately giving rise to widely used applications like ChatGPT. Training these extensive language models typically requires substantial memory capacity. The reason is that this training involves numerous “possibilities.”
For example, when we see a friend looking lovely, we might compliment them by saying, “The necklace you’re wearing today is beautiful, and it matches your outfit perfectly.” However, for AI, after saying, “The necklace you’re wearing today,” it doesn’t know what the next word should be. AI needs extensive training and storage of various potential options to piece together the most accurate response. Otherwise, AI might generate illogical sentences like, “The necklace you’re wearing today, good morning, I love ice cream the most.”
The capacity of CoWoS remains a key factor in whether high-end servers can be delivered smoothly
(Source: Company data, Morgan Stanley Research (e) estimates)
And if we look at the market’s concerns about the investment in generative AI and whether the future demand will stop, Nvidia’s CEO still believes that accelerated computing is the platform transition trend for the entire computer industry, and the demand is just beginning. Investors can also carefully estimate which stage the AI industry is at, from hardware infrastructure to software development, and finally to service generation.
- H100 Solution – L40S
In the previous discussions, we addressed various aspects of H100, and investors may now realize that the issue with H100 lies in the inability of production capacity to keep up with demand. To compensate for the insufficient H100 chip production capacity, Nvidia introduced a new product, L40S, in July this year. It can also perform generative AI and high-performance computing but does not require integration with the scarce HBM memory and CoWoS packaging technology, making it one of the industry’s secret weapons to combat GPU shortages.
However, the computational power of H100 remains irreplaceable. The target customers for L40S will be small and medium-sized enterprises, differing from the original customer base. Therefore, L40S is considered a sub-quality product of the GPU, but it can still effectively alleviate Nvidia’s production capacity pressure.
The current main demand is based on the H100 GPU’s HGX platform, and the new L40S GPU does not require CoWoS packaging. It will be favorable for accelerated computing requirements from the cloud to enterprise, as well as specific applications such as fine-tuning large language models and model inference.
Currently, Nvidia ships three AI servers: H100, A100, and L40S. Regarding the estimated AI server shipments, in the 2023forecast, the high-end AI shipments will be H100 and A100. However, during Nvidia’s latest product launch event, Jensen Huang compared A100 to L40S, leading to speculation that next year’s A100 server may be replaced by L40S.
To achieve Jensen Huang’s vision of “AI for all,” it is essential to make AI services accessible to all businesses. This is the purpose of launching L40S.
L40S’s feature is that the PCIE connector can be directly connected to traditional servers without the need for substantial equipment replacement. The reason is that power and cooling do not require significant changes.
Nvidia also pointed out that L40S and H100 have different orientations. H100 is designed for large language model applications, while L40S can be used for fine-tuning models, including pre-trained models, for small-scale AI training and computing. It is rumored that many companies have already expressed interest.
LOOKING AHEAD TO NVIDIA IN 2023-2024
Looking ahead, Nvidia’s third-quarter financial report is just around the corner. Considering the timeline from semiconductor wafer production to packaging and system assembly, there is typically about aquarter delay. For the H100, in the second and third quarters of 2023, wafer production, packaging, and testing account for approximately 40% and 50% of TSMC’s CoWoS capacity, respectively. If TSMC’s capacity can increase in the future, industry insiders believe that the shipping share of the H100 in Nvidia’s Q3FY24 and Q4FY24 is expected to increase significantly, which would result in the company’s outlook exceeding expectations.
In comparison to the early 2000s when smartphones were just emerging and the demand outlook was still unclear at the time. However, with the release of the first-generation iPhone by Apple in 2007, smartphone applications flourished, and companies in the smartphone supply chain began to benefit. In the long run, the supply chain in the AI sector is expected to benefit from this trend.
Additionally, according to data, the growth potential of edge computing (endpoint computing) is expected to surpass cloud computing in the future. In other words, the future of AI development will focus on the automotive and cloud industries rather than on PCs. However, it’s important to note that the infrastructure for AI servers is not yet fully established, so the opportunities in edge computing are still growing slowly.
As for the industries where edge computing is most widely applied, autonomous driving has the highest growth potential. Companies engaged in IC/IP businesses will pay more attention to the market for custom vehicle chips.
CONCLUSION
Today, we can see that whether it’s Nvidia, Intel, AMD, Apple, or Google, they are all fiercely competing in the battlefield of AI (Artificial Intelligence). Chips have become a globally significant arena, even a focal point of contention between China and the United States. The question remains: How will Nvidia’s path to AI supremacy lead the world forward? Investors from all over the world are eagerly anticipating the answer.
Looking for the latest scoop and cool insights from CoinRank? Hit up our Twitter and stay in the loop with all our fresh stories!

















