KEYTAKEAWAYS
- Origin and Philosophy: Ethereum Classic (ETC) emerged from a 2016 hard fork of Ethereum, maintaining the original blockchain and adhering to the principle of "Code is Law."
- Technical Aspects: ETC uses a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, ensuring secure and immutable transactions, making it a preferred choice for financial operations.
- Future and Community: ETC continues to support a decentralized ecosystem with community-driven development, focusing on smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).

CONTENT
Ethereum Classic (ETC) is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform established in 2016. It supports smart contracts and dApps, adhering to the “Code is Law” principle for secure, immutable transactions.
WHAT IS ETHEREUM CLASSIC (ETC)?
Ethereum Classic (ETC) was established in 2016 and is a decentralized, open-source platform based on blockchain technology. Developers can use this platform to build and deploy smart contracts, as well as host and run decentralized applications (dApps).
Like all other blockchains, ETC maintains a complete record of transaction history in its shared database. Additionally, it records the current state of all smart contracts supported by the blockchain and user balances, which can be digitally transferred to other users’ wallets.
All activities are supported by ERC-20 tokens, which can be mined through a proof-of-work (PoW) process. Due to the split, ETC will not receive updates from ETH 2.0.
- Why did Ethereum Classic emerge?
Ethereum Classic emerged from a hard fork of Ethereum. Initially, the Ethereum blockchain was designed as a single network that facilitated transactions using the cryptocurrency ETH. The network quickly gained popularity, with different teams launching their own tokens on the platform.
In June 2016, a project called The DAO was launched on the platform. The DAO was a decentralized venture fund where investors could vote on assets to invest in. The DAO rapidly accumulated over 11 million ETH from more than 18,000 investors, worth over $150 million at that time.
However, The DAO also attracted the attention of hackers. An unknown hacker discovered a vulnerability in the smart contract, enabling them to extract about one-third of the ETH accumulated by The DAO.
To recover the losses, the Ethereum community and foundation initiated a vote, deciding to perform a hard fork on the original Ethereum mainnet to restore the stolen funds. 97% of the community members voted in favor of this hard fork, leading to the formation of the current Ethereum (ETH).
However, a portion of the community believed that a blockchain, once launched, should be immutable like Bitcoin and should not be altered due to hacker attacks. They continued to support the original Ethereum mainnet, now known as Ethereum Classic (ETC).
As a result, the Ethereum blockchain split into two independent networks. The newer network inherited the Ethereum name and uses ETH as its cryptocurrency, while the original network is called Ethereum Classic and uses ETC as its cryptocurrency.
>>> More to read : What Is Ethereum & How Does It Work?
ETC VS ETH
Although ETC and ETH share a common ancestor, they have diverged significantly in various aspects since the fork. Here are the specific differences:
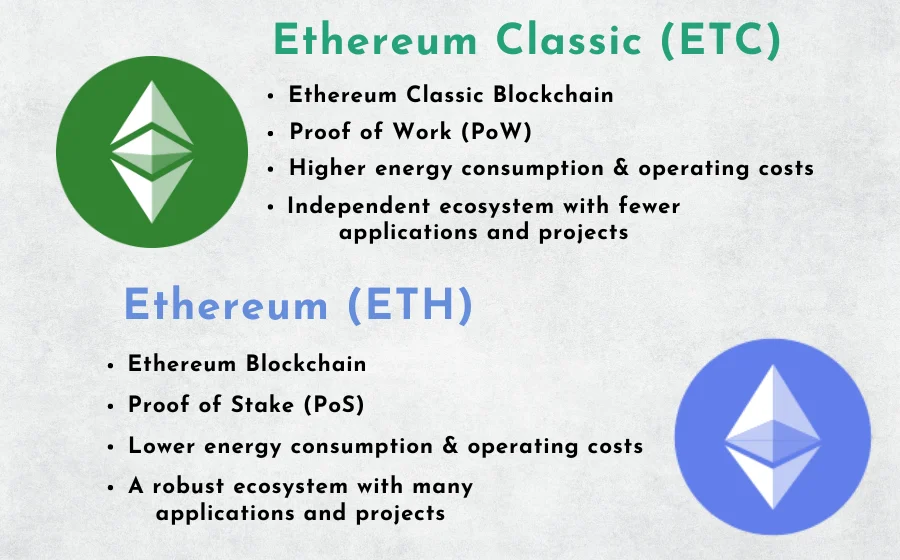
THE FUTURE OF ETC
The ETC blockchain and ETC continue to adhere to the principle of “Code is Law.” This means that applications run exactly as programmed, without downtime, censorship, or third-party interference. Ethereum Classic is the only major smart contract platform that has proven its ability to uphold this commitment.
ETC‘s core propositions for its future development are as follows:
1. Blockchain technology and smart contracts have the potential to unlock human prosperity.
2. The value introduced by a smart contract platform lies in the principle of “Code is Law,” which enables the construction of unstoppable applications.
3. Actively embracing “Code is Law” will bring immense benefits; those who attempt to hinder its adoption will be left behind.
4. Transformation can potentially disrupt powerful institutions, which may resist technologies threatening their status.
5. Only blockchains that adhere to the “Code is Law” commitment can meet this challenge; others will be constrained.
6. Today, most blockchain projects, including Ethereum (ETH), do not uphold the “Code is Law” principle, weakening the value they claim to offer.
ETHEREUM CLASSIC FEATURE
- Immutability and Censorship Resistance
Ethereum Classic is a secure and transparent public blockchain. Transactions on its immutable and censorship-resistant blockchain cannot be edited or deleted, making it an ideal choice for financial transactions.
- Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications
Ethereum Classic supports smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts capable of automatically carrying out complex processes. It also supports and promotes the construction of decentralized applications (dApps).
- Interoperability
Ethereum Classic can interoperate with other blockchains, allowing communication, value exchange, and resource sharing between Ethereum Classic and other blockchain networks.
- Community-Driven Development
Ethereum Classic is an open-source project managed by a decentralized community. This allows for continuous improvement through community-proposed and implemented new features and upgrades.
Overall, Ethereum Classic is a secure and versatile platform for building dApps and smart contracts. Its features of immutability, censorship resistance, interoperability, and community-driven development make it an attractive investment opportunity.
>>> More to read : What is Altcoin & Altcoin Season?
FAQ
- What is Ethereum Classic?
Ethereum Classic is the “unforked” original blockchain from the Ethereum fork.
▶ Buy Crypto at Bitget
ꚰ CoinRank x Bitget – Sign up & Trade to get $20!

















