KEYTAKEAWAYS
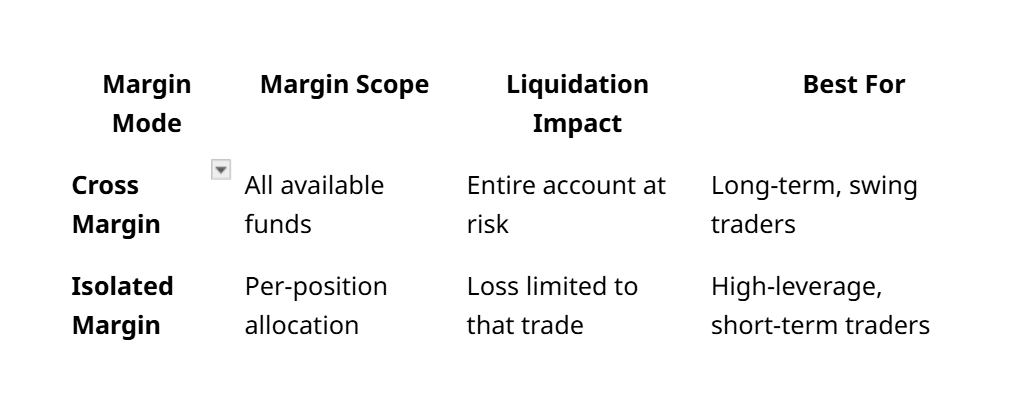
- Cross Margin allows all positions to share account funds, offering higher capital efficiency but increasing the risk of full account liquidation.
- Isolated Margin contains risk to individual trades, making it ideal for short-term strategies and precise risk control, though with lower capital flexibility.
- Choosing the right margin mode depends on your trading style and risk tolerance; many traders combine both for strategic balance.

CONTENT
Learn the difference between Cross Margin and Isolated Margin in crypto trading. Understand how each margin mode impacts risk, capital efficiency, and trading strategies.
WHAT IS CROSS MARGIN?
🔍 Shared Risk Across Your Entire Account
In crypto futures trading, Cross Margin refers to a system where all of your available funds in the account are shared as collateral across open positions. This means that if one position starts to incur losses, the platform will automatically draw from your remaining balance to prevent liquidation.
The main advantage of Cross Margin is its higher tolerance to market volatility. It’s particularly suitable for long-term traders who want more breathing room in their positions without having to constantly monitor margin levels or manually add collateral.
However, the trade-off is that your entire balance is at risk. If a heavily leveraged position moves against you significantly, the loss could wipe out all the funds in your account. This makes Cross Margin riskier in terms of potential overall capital exposure.
>>> More to read: What is Margin Trading: A Comprehensive Introduction
WHAT IS ISOLATED MARGIN?
🔍 Independent Risk Per Position
By contrast, Isolated Margin mode treats each position as a separate entity. Only the margin you allocate to a specific position will be at risk, while the rest of your account remains untouched—even if that position gets liquidated.
This setup allows for better risk control. If you’re trading with high leverage or experimenting with volatile assets, Isolated Margin ensures that any potential loss is limited to a predefined amount. It’s particularly useful for short-term traders who want to cap their exposure per trade.
One downside of Isolated Margin is that it doesn’t automatically pull in extra margin from your account when a position is at risk. If you’re not actively monitoring your trade or don’t top up the margin in time, the position may get liquidated quickly.
>>> More to read: Crypto Trading Strategies for Beginners 2025
ISOLATED MARGIN PROS AND CONS
Isolated Margin is a risk-separation strategy where traders allocate a specific amount of margin to each position. This ensures that each trade’s profit or loss is calculated independently, offering precise control over individual positions.
✅ Pros:
- Stronger Risk Control: With Isolated Margin, losses are limited to the margin assigned to a specific position. A single bad trade won’t affect the rest of your account.
- Diversified Strategy Friendly: Since each position is isolated, traders can spread risk across multiple assets without fear of one trade dragging down the entire portfolio.
- High Transparency: Profits and losses are clearly separated per trade, making it easier to review strategies and adjust accordingly.
❌ Cons:
- Lower Capital Efficiency: Funds are locked into individual trades, which may leave idle capital that could have been used more effectively in a Cross Margin system.
- Higher Management Complexity: Traders must manage and monitor each position’s margin separately, which can be overwhelming for beginners or passive investors.
- Limited Upside Potential: Because leverage is restricted by the isolated margin assigned, the potential for amplified gains is lower compared to Cross Margin.
>>> More to read: What is Crypto Closing Position? Is It the Same as Selling?
CROSS MARGIN PROS AND CONS
Cross Margin is a more flexible model where all available funds in your account are pooled together to support all open positions. This setup is ideal for larger accounts and longer-term strategies.
✅ Pros:
- Efficient Capital Use: All positions can draw from a shared pool of funds, maximizing margin utility and supporting larger or multiple positions simultaneously.
- Simplified Operation: There’s no need to manage margin for each position separately, making the process smoother and less time-consuming.
❌ Cons:
- Concentrated Risk: A significant loss in one position can deplete the entire account, as all funds are exposed to risk across trades.
- Harder Risk Control: Individual risk limits per position can’t be easily enforced, which may be problematic for traders needing precise risk-to-reward ratios.
- Higher Liquidation Risk: In fast-moving markets, the shared margin pool can get drained quickly, leading to forced liquidation of multiple positions if not actively monitored.
>>> More to read: Crypto Spot Trading vs. Future Trading: Which is Best for You?
CHOOSING THE RIGHT MODE: RISK PROFILE & STRATEGY MATTER
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to whether Cross Margin or Isolated Margin is better. Your choice should depend on your trading strategy, risk tolerance, and how hands-on you are with trade management.
If you prefer swing or long-term trades and have a larger capital base, Cross Margin can give you more flexibility. On the other hand, if you’re into scalping, high leverage trading, or you want to set clear loss limits, Isolated Margin is a safer choice.
In fact, many advanced traders use both modes simultaneously in a hybrid approach—allocating key positions to Cross Margin while experimenting or hedging with Isolated Margin. This allows you to balance risk exposure while optimizing capital usage.
▶ Buy Crypto at Bitget
ꚰ CoinRank x Bitget – Sign up & Trade!


















