KEYTAKEAWAYS
- Social engineering attack on DMM Bitcoin resulted in the theft of 4,502.9 BTC and stricter regulations by Japan’s FSA.
- Phishing exploited PlayDapp’s smart contract vulnerabilities, causing $230 million in losses and highlighting the need for stronger contract security.
- Vulnerabilities in WazirX’s multi-signature wallets led to major losses, leading to improved integration protocols and better wallet security measures.

- KEY TAKEAWAYS
- 1. DMM BITCOIN: A CLASSIC CASE OF SOCIAL ENGINEERING ATTACK
- 2. PLAYDAPP: THE COST OF SMART CONTRACT VULNERABILITIES
- 3. WAZIRX: THE HIDDEN RISKS OF MULTI-SIGNATURE WALLETS
- 4. MUNCHABLES: THE THREAT OF INSIDER ATTACKS
- 5. BINGX: NORTH KOREAN HACKERS’ COMPLEX MONEY LAUNDERING TACTICS
- CONCLUSION
- DISCLAIMER
- WRITER’S INTRO
CONTENT
Explore the top five blockchain security incidents of 2024, including social engineering, smart contract vulnerabilities, and insider attacks, resulting in over $2 billion in losses and challenging the industry’s security standards.
In 2024, the blockchain industry made significant strides in technological innovation and market expansion. However, security vulnerabilities continued to pose significant threats to the industry’s development.
Throughout the year, the industry recorded 410 security incidents, resulting in losses of $2.013 billion. Among these incidents, five major security attacks stood out due to their substantial financial impact and the sophisticated methods employed by attackers.
These incidents not only caused significant damage to the affected projects and teams but also challenged the trust and reputation of the entire blockchain ecosystem.
This article examines these five critical security incidents, analyzing their attack vectors, immediate impacts, and broader implications for the industry.
Through this analysis, we aim to provide valuable insights for industry practitioners and users while emphasizing the urgent need for enhanced security measures across the blockchain sector.
1. DMM BITCOIN: A CLASSIC CASE OF SOCIAL ENGINEERING ATTACK
On May 31, 2024, attackers targeted Japan’s DMM Bitcoin exchange through a sophisticated social engineering scheme. The attackers posed as LinkedIn recruiters, distributing a malicious Python script disguised as an onboarding test to exchange employees.

Upon execution, the script compromised session cookie information, enabling attackers to impersonate legitimate employees. The breach resulted in the theft of 4,502.9 BTC (approximately $482 million), marking it as Japan’s third-largest cryptocurrency exchange hack.
The attackers successfully altered transaction requests and transferred funds to wallets under their control. The incident prompted Japan’s Financial Services Agency (FSA) to implement stricter regulations on cryptocurrency exchanges, mandating comprehensive security reassessments across all platforms.
2. PLAYDAPP: THE COST OF SMART CONTRACT VULNERABILITIES
On February 9, 2024, attackers compromised PlayDapp’s blockchain gaming platform through a targeted phishing campaign. After successfully obtaining administrator private keys through malicious software, the attackers modified the smart contract’s ownership and minting permissions.

The attack resulted in $230 million in losses through the unauthorized minting of 200 million PLA tokens. Despite offering a $1 million white-hat reward, PlayDapp failed to recover the stolen funds. The incident severely impacted PlayDapp’s token value and user confidence, highlighting the critical importance of robust smart contract security measures.
3. WAZIRX: THE HIDDEN RISKS OF MULTI-SIGNATURE WALLETS
On July 18, 2024, attackers exploited vulnerabilities in WazirX’s multi-signature wallet system. The attack targeted the integration between WazirX’s six-signatory system and their third-party service provider, Liminal.
The breach resulted in losses exceeding $230 million. Attackers successfully bypassed security measures by manipulating transaction payload verification processes. WazirX responded by strengthening its third-party service provider integration protocols and implementing enhanced wallet security mechanisms.
4. MUNCHABLES: THE THREAT OF INSIDER ATTACKS
On March 27, 2024, a malicious actor infiltrated the Munchables project team within the Blast ecosystem. Operating under the guise of a developer, the attacker gained access to core code and security credentials.
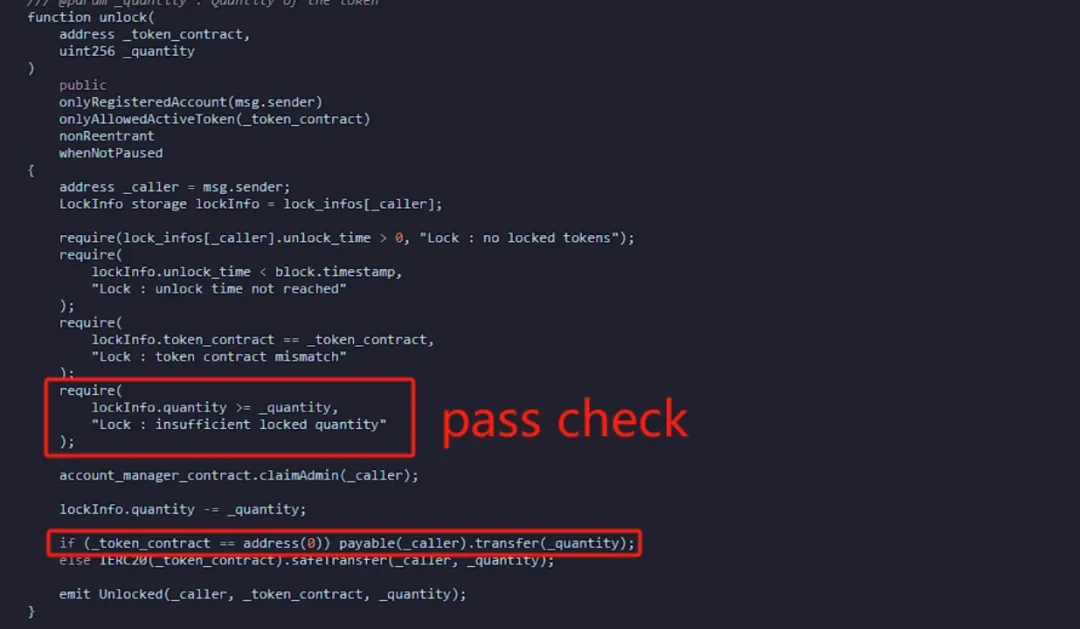
The attack initially resulted in losses of $62.5 million through unauthorized smart contract manipulation. In a notable turn of events, Blast founder Pacman successfully negotiated the complete return of stolen funds through community and team pressure, though the incident highlighted significant vulnerabilities in developer access management.
5. BINGX: NORTH KOREAN HACKERS’ COMPLEX MONEY LAUNDERING TACTICS
On September 20, 2024, attackers compromised BingX’s primary digital asset storage (hot wallet). The attack bore hallmarks of the North Korean hacker group Lazarus Group, known for targeting cryptocurrency platforms.

The breach resulted in approximately $45 million in losses, with stolen funds being laundered through multiple blockchain networks and mixing services like Tornado Cash. BingX responded by enhancing its wallet security infrastructure and partnering with blockchain analytics firms to track compromised assets.
CONCLUSION
The top five security incidents of 2024 served as a wake-up call for the blockchain industry. These events not only exposed the industry’s shortcomings in security protection but also reminded practitioners and users of the need to strengthen security awareness.
Whether it was smart contract vulnerabilities, social engineering attacks, or insider threats, these incidents underscored the complexity and diversity of blockchain security challenges.As technology continues to evolve, strategies for protecting it must advance accordingly. Key steps include:
Strengthening Regulatory Frameworks: Governments and regulatory bodies must work closely with the blockchain industry to establish and enforce robust security standards. The Japanese Financial Services Agency’s (FSA) response to the DMM Bitcoin hack serves as a positive example of regulatory intervention driving improvements in security practices.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: The blockchain community must foster greater collaboration and information sharing to combat emerging threats. Initiatives like threat intelligence sharing platforms and industry-wide security task forces can play a critical role in this regard.
Investing in Security Research and Development: Continuous investment in security research and development is crucial for staying ahead of attackers. Innovations in cryptographic technologies, consensus mechanisms, and decentralized identity solutions contribute to building a more secure blockchain ecosystem.
User Education and Awareness: Finally, users must be educated about risks and best practices for protecting digital assets. From recognizing phishing attacks to understanding the importance of private key management, user awareness is a key line of defense.
In summary, although the blockchain industry made significant progress in 2024, the security incidents of the year remind us that challenges lie ahead. By learning from these events and taking proactive measures to enhance security, the industry can build a more resilient and trustworthy ecosystem.
The path forward may be challenging, but with collective effort and innovation, the blockchain industry can continue to thrive while safeguarding user assets and trust.
Also Read:
DEXX Hacked Shocking the Entire Network: How to Avoid Becoming the Next Victim?
Why Have Nations Been Reluctant to Include Bitcoin in National Reserves?
▶ Buy Crypto at Bitget
CoinRank x Bitget – Sign up & Trade to get $20!













